Stepper motor AC or DC?: Stepper motors are versatile components used in various precision applications, and understanding whether they are AC or DC is essential for proper use and integration. Here’s a detailed discussion of whether stepper motors are AC or DC, and how they operate:
Stepper Motors: AC or DC?
Stepper motors are classified as DC (Direct Current) motors. However, their operation involves complex electrical control that differentiates them from simple DC motors.
Why Stepper Motors are Considered DC:
- Power Supply:
- DC Voltage: Stepper motors are typically powered by a DC voltage source. This is the voltage provided by the power supply or battery that is connected to the motor driver or controller.
- Voltage Regulation: While the motor itself operates on DC power, the stepper motor driver may use techniques to regulate the voltage and control the current supplied to the motor. This often involves stepping up the voltage and using pulse-width modulation (PWM) to manage power delivery.
- Motor Operation:
- Electromagnetic Induction: Stepper motors operate based on electromagnetic induction created by DC current flowing through their windings. The current generates a magnetic field that moves the rotor in discrete steps.
- Control Signals: The motor’s movement is controlled by a series of electrical pulses or step signals, which are also DC in nature. The motor driver converts these pulses into appropriate currents for the motor windings.
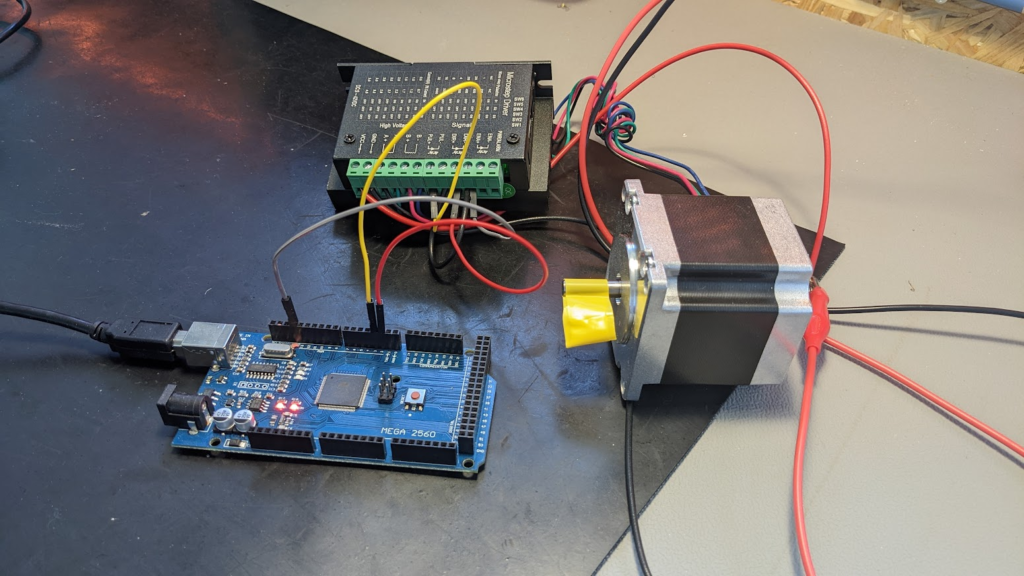
Stepper motor AC or DC: Stepper Motor Drivers
- Driver Function:
- Pulse Generation: The stepper motor driver generates a sequence of electrical pulses that determine the motor’s steps and direction of rotation. These pulses are based on a DC power supply.
- Current Regulation: Drivers use DC voltage but employ sophisticated techniques to regulate current, such as chopper drives or microstepping, to ensure the motor operates efficiently and within its specifications.
- Power Supply:
- Higher Voltage: To enhance performance, stepper motor drivers often use higher DC voltages than the motor’s rated voltage. This helps in achieving better torque and speed characteristics. The driver converts this higher voltage to the appropriate current for the motor.
Stepper motor AC or DC: Comparison with AC Motors:
- AC Motors:
- Alternating Current: AC motors run on alternating current (AC) and are powered directly by AC mains or generators. They are generally used in applications where continuous rotation and high power are required, such as in household appliances and industrial machines.
- Stepper Motors vs. AC Motors:
- Control: Stepper motors are designed for precise control and positioning, making them ideal for applications requiring accurate movement. AC motors are typically used for applications requiring continuous rotation and less precise control.
Practical Implications:
- Applications:
- Stepper Motors: Used in applications such as 3D printers, CNC machines, robotics, and automated systems where precise control and positioning are crucial.
- AC Motors: Used in applications like fans, pumps, and conveyor belts where continuous rotation and higher power are needed.
- Driver and Controller:
- Ensure that you use a compatible stepper motor driver with your motor to handle the DC power supply and control signals correctly.
Conclusion
Stepper motors are classified as DC motors due to their reliance on DC voltage for operation and the nature of their control signals. Although they are powered by DC, their operation involves sophisticated drivers and controllers that manage the current and generate precise step signals for accurate movement.

