Torque is a crucial parameter for stepper motors, as it determines their ability to perform work and handle loads. Understanding stepper motor torque helps in selecting the right motor for your application and ensuring it operates effectively. This article will explain the concept of torque in stepper motors, the factors influencing it, and how to determine the appropriate torque for your needs.
What is Stepper Motor Torque?
Torque refers to the rotational force that a motor can exert. For stepper motors, torque is critical because it affects the motor’s ability to move loads and achieve precise positioning. There are two primary types of torque associated with stepper motors:
- Holding Torque: The maximum torque the motor can produce when stationary, with no movement. It is important for maintaining the motor’s position under load.
- Dynamic Torque: The torque available while the motor is in motion. It is usually lower than the holding torque due to factors such as inertia and friction.
Measuring Stepper Motor Torque
Torque is measured in units such as Newton-meters (Nm) or ounce-inches (oz-in). The measurement of torque is typically provided in the motor’s datasheet and is crucial for ensuring the motor can handle the intended load.
Factors Affecting Stepper Motor Torque
- Motor Size and Design
- Size: Larger stepper motors generally have higher torque capabilities due to their increased physical dimensions and greater magnetic field strength.
- Design: The design of the motor, including the number of poles and the winding configuration, influences its torque characteristics.
- Current and Voltage Supply
- Current: The amount of current supplied to the motor affects the torque. Higher current levels can increase the motor’s torque, but it must be within the motor’s rated limits to avoid overheating.
- Voltage: While the voltage rating does not directly determine torque, higher voltages can improve performance by allowing the motor to reach higher speeds and better torque at higher speeds, due to increased current flow.
- Stepper Motor Type
- Unipolar Motors: Typically have lower torque compared to bipolar motors but are simpler to drive.
- Bipolar Motors: Offer higher torque and better performance by using both windings to create a stronger magnetic field.
- Step Angle and Microstepping
- Step Angle: Motors with smaller step angles (e.g., 1.8°) generally offer higher torque per step compared to those with larger step angles.
- Microstepping: Using microstepping can affect the effective torque by dividing each full step into smaller steps, which can improve resolution but may reduce the available torque at each microstep.
- Load and Mechanical Factors
- Load: The amount of load applied to the motor affects its performance. Exceeding the motor’s torque capacity can result in missed steps and reduced accuracy.
- Mechanical Efficiency: Friction, mechanical alignment, and other factors in the system can impact the effective torque available to the load.
Also Read: Stepper Motor RPM – How to Calculate?
Calculating Torque
To calculate the torque required for a specific application, you need to consider the following:
- Load Requirements: Determine the load that the stepper motor needs to handle. This includes factors such as weight, resistance, and required movement.
- Motor Specifications: Refer to the motor’s datasheet for the holding torque and dynamic torque values.
- Calculation Formula: Torque can be calculated using the formula:
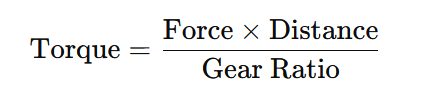
Where:
- Force is the load being moved.
- Distance is the radius at which the force is applied (e.g., from the center of the motor).
- Gear Ratio adjusts for any mechanical gearing used in the system.
Example
Suppose you have a stepper motor with a holding torque of 1 Nm and you need to move a load requiring 0.5 Nm of torque. The motor’s torque rating is adequate for this application. If the load requires 2 Nm of torque, you would need a motor with a higher torque rating or consider reducing the load or using mechanical gearing to adjust the torque requirements.
Conclusion
The torque of a stepper motor is a critical factor that determines its ability to handle loads and perform precise movements. By understanding the concepts of holding torque and dynamic torque, and considering factors such as motor size, current, voltage, and mechanical efficiency, you can select the right stepper motor for your application. Properly calculating and matching the motor’s torque to your requirements ensures reliable performance and accuracy in your systems.

